
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Fetal Abdominal Obesity Detected at 24 to 28 Weeks of Gestation Persists until Delivery Despite Management of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:547-57)
- Wonjin Kim, Soo Kyung Park, Yoo Lee Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):970-971. Published online November 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0253
- 2,449 View
- 68 Download
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
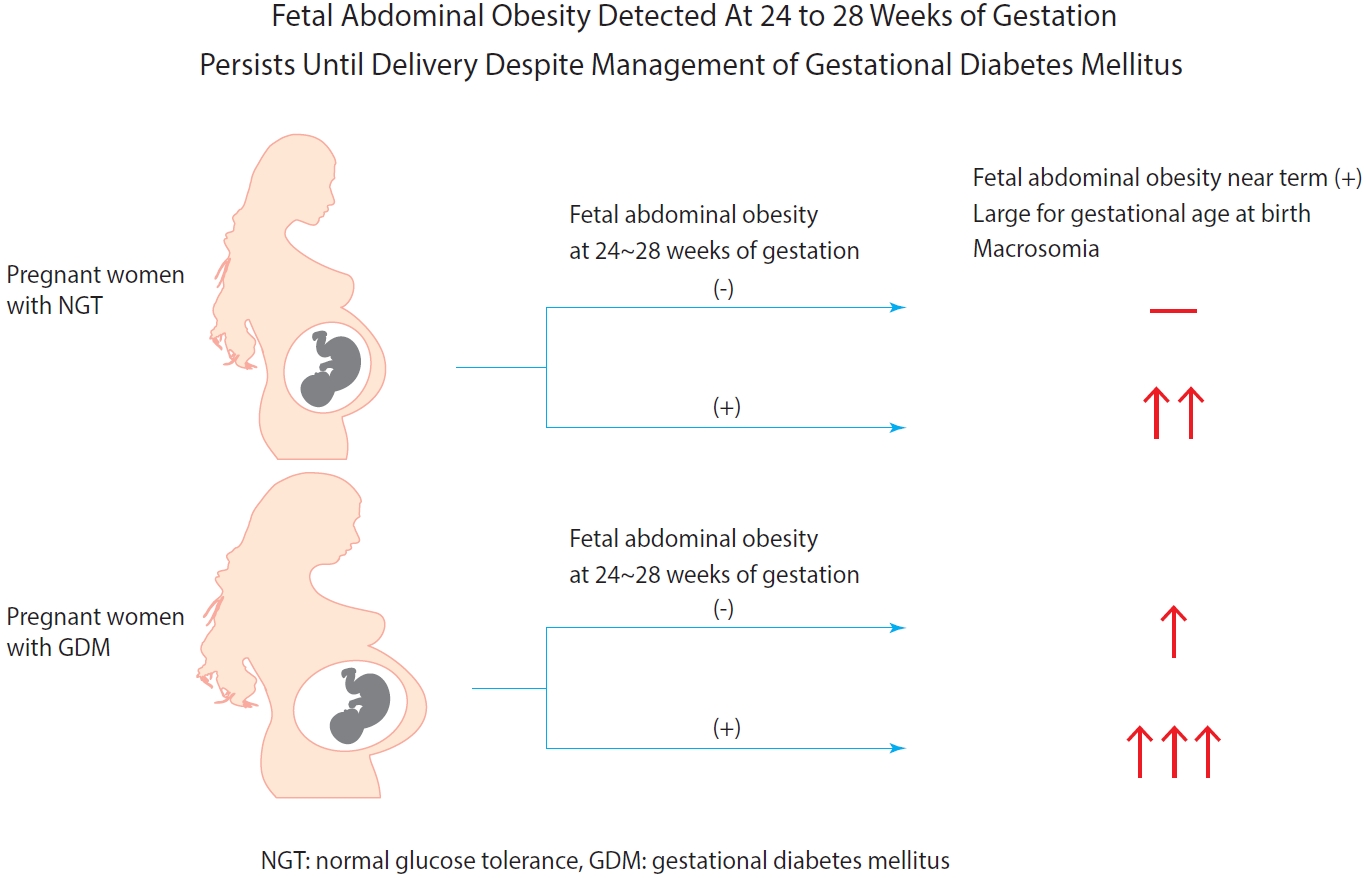
- Fetal Abdominal Obesity Detected At 24 to 28 Weeks of Gestation Persists Until Delivery Despite Management of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Wonjin Kim, Soo Kyung Park, Yoo Lee Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):547-557. Published online March 5, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0078
- 5,862 View
- 185 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Fetal abdominal obesity (FAO) has been reported to be affected at gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) diagnosis at 24 to 28 weeks of gestation in older and/or obese women. This study investigated whether the management of GDM improves FAO in GDM subjects near term.
Methods
Medical records of 7,099 singleton pregnant women delivering at CHA Gangnam Medical Center were reviewed retrospectively. GDM was diagnosed by 100-g oral glucose tolerance test after 50-g glucose challenge test based on Carpenter–Coustan criteria. GDM subjects were divided into four study groups according to maternal age and obesity. FAO was defined as ≥90th percentile of fetal abdominal overgrowth ratios (FAORs) of the ultrasonographically estimated gestational age (GA) of abdominal circumference per actual GA by the last menstruation period, biparietal diameter, or femur length, respectively.
Results
As compared with normal glucose tolerance (NGT) subjects near term, FAORs and odds ratio for FAO were significantly higher in old and/or obese women with GDM but not in young and nonobese women with GDM. For fetuses of GDM subjects with FAO at the time of GDM diagnosis, the odds ratio for exhibiting FAO near term and being large for GA at birth were 7.87 (95% confidence interval [CI], 4.38 to 14.15) and 10.96 (95% CI, 5.58 to 20.53) compared with fetuses of NGT subjects without FAO at GDM diagnosis.
Conclusion
Despite treatment, FAO detected at the time of GDM diagnosis persisted until delivery. Early diagnosis and treatment might be necessary to prevent near term FAO in high-risk older and/or obese women. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effects of gestational diabetes mellitus on fetal growth: is it different for low-risk and medium–high-risk pregnant women?
Jie Wang, Xin Cheng, Zhen-Hua Li, Yi-Cheng Mao, Xin-Qiang Wang, Kang-Di Zhang, Wen-Jie Yu, Ying-Qing Li, Jia-wen Zhao, Mao-Lin Chen, Guo-peng Gao, Cheng-Yang Hu, Xiu-Jun Zhang
Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Fetal abdominal obesity and the ensuing adverse perinatal outcomes in older obese pregnant women with or without obesity and with normal glucose tolerance
Wonjin Kim, Soo Kyung Park, Yoo Lee Kim
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Early-life exposure to gestational diabetes mellitus predisposes offspring to pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Qian-Ren Zhang, Yan Dong, Jian-Gao Fan
Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Gestational diabetes mellitus and adverse pregnancy outcomes: systematic review and meta-analysis
Wenrui Ye, Cong Luo, Jing Huang, Chenglong Li, Zhixiong Liu, Fangkun Liu
BMJ.2022; : e067946. CrossRef - Fetal abdominal overgrowth is already present at 20–24 gestational weeks prior to diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus
Wonjin Kim, Soo Kyung Park, Yoo Lee Kim
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- The effects of gestational diabetes mellitus on fetal growth: is it different for low-risk and medium–high-risk pregnant women?
- The Glycated Albumin to Glycated Hemoglobin Ratio Might Not Be Associated with Carotid Atherosclerosis in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
- Wonjin Kim, Kwang Joon Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(6):456-463. Published online December 15, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.6.456
- 4,133 View
- 33 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The ratio of glycated albumin to glycated hemoglobin (GA/A1c) is known to be elevated in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) who had decreased insulin secretion. Additionally, the carotid intima media thickness (IMT) is greater in T2DM patients with higher GA/A1c ratios. We investigated whether increased GA/A1c ratio and IMT are also associated in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM), which is characterized by lack of insulin secretory capacity.
Methods In this cross-sectional study, we recruited 81 T1DM patients (33 men, 48 women; mean age 44.1±13.0 years) who underwent carotid IMT, GA, and HbA1c measurements.
Results The mean GA/A1c ratio was 2.90. Based on these results, we classified the subjects into two groups: group I (GA/A1c ratio <2.90,
n =36) and group II (GA/A1c ratio ≥2.90,n =45). Compared with group I, the body mass indexes (BMIs), waist circumferences, and IMTs were lower in group II. GA/A1c ratio was negatively correlated with BMI, urine albumin to creatinine ratio (P <0.001 for both), and both the mean and maximal IMT (P =0.001, both). However, after adjusting the confounding factors, we observed that IMT was no longer associated with GA/A1c ratio.Conclusion In contrast to T2DM, IMT was not significantly related to GA/A1c ratio in the subjects with T1DM. This suggests that the correlations between GA/A1c ratio and the parameters known to be associated with atherosclerosis in T2DM could be manifested differently in T1DM. Further studies are needed to investigate these relationships in T1DM.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Glycated Albumin and Glycated Albumin/HbA1c Predict the Progression of Coronavirus Disease 2019 from Mild to Severe Disease in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Jeongseon Yoo, Youngah Choi, Shin Ae Park, Ji Yeon Seo, Chul Woo Ahn, Jaehyun Han
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(9): 2327. CrossRef - Variability in glycated albumin levels predicts the progression of diabetic nephropathy
Su Bin Park, Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim, Yoon Jeong Nam, Kang Hee Ahn, Jong Ho Kim, Yun Kyung Jeon, Bo Hyun Kim, Sang Heon Song, Ihm Soo Kwak, Eun Kyung Lee, Yong Ki Kim
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2017; 31(6): 1041. CrossRef - Significant liver fibrosis assessed using liver transient elastography is independently associated with low bone mineral density in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Gyuri Kim, Kwang Joon Kim, Yumie Rhee, Sung-Kil Lim, Salvatore Petta
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(7): e0182202. CrossRef - Determinants of Preclinical Atherosclerosis Are Different in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetic Women
P. PIŤHOVÁ, K. ŠTECHOVÁ, J. PIŤHA, V. LÁNSKÁ, M. KVAPIL
Physiological Research.2016; : 219. CrossRef - Characteristics Predictive for a Successful Switch from Insulin Analogue Therapy to Oral Hypoglycemic Agents in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Gyuri Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee, Byung-Wan Lee
Yonsei Medical Journal.2016; 57(6): 1395. CrossRef - Visceral adiposity is associated with altered myocardial glucose uptake measured by 18FDG-PET in 346 subjects with normal glucose tolerance, prediabetes, and type 2 diabetes
Gyuri Kim, Kwanhyeong Jo, Kwang Joon Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Eugene Han, Hye-jin Yoon, Hye Jin Wang, Eun Seok Kang, Mijin Yun
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycated albumin and the risk of micro- and macrovascular complications in subjects with Type 1 Diabetes
Hye-jin Yoon, Yong-ho Lee, So Ra Kim, Tyler Hyungtaek Rim, Eun Young Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee, Byung-Wan Lee
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Candidate Pairs of Hydrolytic Enzymes for Spectrophotometric-dual-enzyme-simultaneous-assay
Hongbo Liu, Mei Yuan, Xiaolan Yang, Xiaolei Hu, Juan Liao, Jizheng Dang, Yanling Xie, Jun Pu, Yuanli Li, Chang-Guo Zhan, Fei Liao
Analytical Sciences.2015; 31(5): 421. CrossRef - Glycated Albumin Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Increase Relative to HbA1cwith Time
Hye-jin Yoon, Yong-ho Lee, Kwang Joon Kim, So Ra Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee, Byung-Wan Lee
BioMed Research International.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Association of hemoglobin A1c and glycated albumin with carotid atherosclerosis in community-dwelling Japanese subjects: the Hisayama Study
Naoko Mukai, Toshiharu Ninomiya, Jun Hata, Yoichiro Hirakawa, Fumie Ikeda, Masayo Fukuhara, Taeko Hotta, Masafumi Koga, Udai Nakamura, Dongchon Kang, Takanari Kitazono, Yutaka Kiyohara
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2015;[Epub] CrossRef
- Glycated Albumin and Glycated Albumin/HbA1c Predict the Progression of Coronavirus Disease 2019 from Mild to Severe Disease in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





